October 31, 2024
What is APS-C size? Explanation of the differences and advantages from full-size lenses
What is APS-C size? Explanation of the differences and advantages from full-size lenses


Cameras with APS-C sensors are more compact and handy than cameras with full-size sensors, and are widely used by both beginners and professionals. On the other hand, there may be some unexpected differences between APS-C size and full-size cameras, as well as how to select lenses. This article provides a wide range of explanations, from basic knowledge of the APS-C size to the advantages of using it and suitable shooting situations.
What is APS-C size?
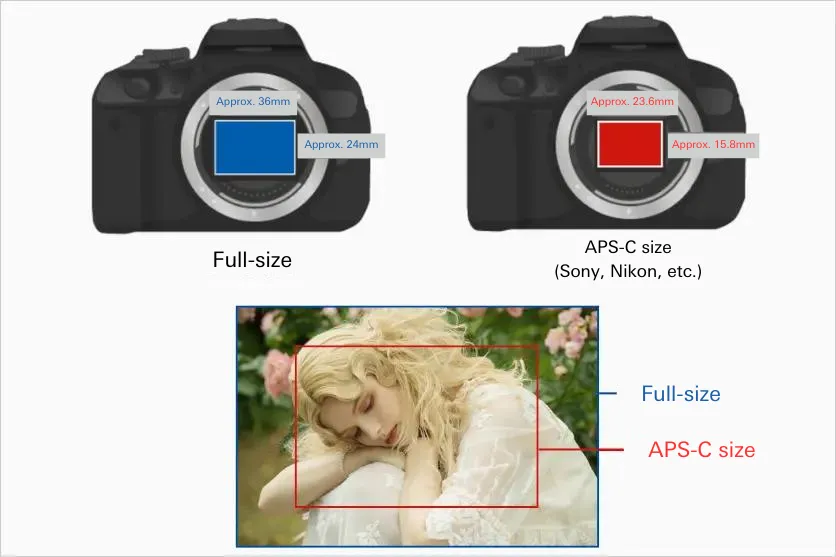
APS-C size is one of the image sensor size standards for interchangeable-lens cameras. It is called APS-C size because it has a sensor size (approximately 24 mm x 16 mm) similar to the APS-C (Advanced Photo System type-C) film format among film cameras. However, since there is no strict size standard, the sensor size differs slightly among camera manufacturers. For example, Nikon (DX format) and Sony have a sensor size of approximately 23.6 mm x 15.8 mm, while Canon has a sensor size of approximately 22.3 mm x 14.9 mm.
Differences between APS-C size and full-size
There are several types of sensor sizes for interchangeable-lens cameras, but generally APS-C size or full-size is the most common. There are differences between APS-C size and full-size in terms of sensor size, angle of view, bokeh, dynamic range, high sensitivity shooting, and size. These also lead to their characteristics. Let's take a closer look at the differences between them.
Sensor size
There is a big difference in sensor size between full-size and APS-C size cameras. The full-size sensor is approximately 35 mm x 24 mm, while the APS-C sensor is approximately 23.6 mm x 15.8 mm. This difference affects the appearance and angle of view of the photos we will introduce next.
Angle of view
When photographing a subject from the same location using the same lens, the area captured in a photo with an APS-C size camera will be narrower than with a full-size camera. This is because the APS-C size sensor is smaller than the full-size sensor and can only receive a portion of the light coming through the lens.
As a result, images taken with an APS-C size camera look about 1.5 to 1.6 times larger (sometimes called the “telephoto effect” because the image appears to be magnified like a telephoto lens).
Bokeh effect
When the same subject is photographed at the same angle of view, the bokeh effect appears larger with a full-size camera than with an APS-C size camera. This is because the APS-C size sensor is smaller than the full-size, resulting in a deeper depth of field.
Depth of field refers to the area that appears to be in focus in a photograph, and since the APS-C size sensor has a wider area in focus than the full-size sensor, the amount of blur in the background appears smaller.
Dynamic Range (smoothness of lightness, darkness and gradation)
The range of brightness and darkness that can be recognized by the sensor is called dynamic range. The wider the dynamic range, the less likely it is that whites will be blown out or blacks will be blurred, and the more beautifully and smoothly light/dark differences and gradations (tones) can be expressed in a single photo. Generally, the larger the sensor size, the wider the dynamic range.
Therefore, the full-size sensor tends to produce more beautiful tonal gradations than the APS-C size sensor. This is because the larger the sensor size, the lighter each pixel (pixel) in the sensor receives.
High-sensitivity photography in dark environments
When shooting in dark environments, exposure is secured by increasing the ISO sensitivity, but if the ISO sensitivity is raised too high, noise may become noticeable. As mentioned above, the full-size sensor has a larger sensor size than the APS-C size, allowing it to receive more light.
As a result, even when shooting at the same ISO sensitivity, the full-size sensor can produce less noise. For this reason, full-size cameras are said to be more likely to produce high-quality images when shooting at high sensitivities in dark locations.
Size and weight
Because the sensor size of APS-C size cameras is smaller than that of full-size cameras, both the body and lens are often compact and lightweight. This leads to ease of carrying when heading out to shoot and ease of handling while shooting. APS-C size cameras are especially useful for those who frequently travel or shoot outdoors and want to keep their luggage compact.
However, recent technological advances have made it possible to produce compact full-size cameras. Therefore, it is important to note that “full-size camera = large” does not always mean “large”.
Advantages of APS-C size cameras
APS-C size cameras have several unique advantages over full-size cameras. Here are some typical advantages.
Able to magnify the subject
As mentioned above, the angle of view of an APS-C size camera is narrower than that of a full-size camera, and the subject appears greatly magnified (when shot from the same position with a lens of the same focal length). Therefore, the advantage of the APS-C size is that it is easier to take a large picture of the subject. This telephoto lens-like feature has led some professional photographers to choose APS-C size cameras.
Compact and easy to handle
Compared to full-size cameras, many APS-C size cameras are lighter and more compact. For this reason, APS-C size cameras are easy to use when you want to lighten your footwork for long-time carrying, mountain climbing, or traveling.
Lenses for APS-C size cameras also tend to be more compact than those for full-size cameras, so the entire camera and lens set-up is more portable.
Easy for beginners to get started
APS-C size cameras tend to be more reasonably priced than their full-size counterparts. This has the advantage of making it easy for people who are new to interchangeable-lens cameras to get started. Also, as mentioned above, APS-C size cameras are compact and easy to handle, making them easy to take with you.
This ease of use is an advantage for beginners, as it is important for them to accumulate experience in taking pictures to improve their skills.
Scenes you want to shoot with an APS-C size camera
Many people may be under the impression that APS-C size cameras are inferior to full-size cameras in terms of image quality, but even photos taken with APS-C size cameras can be of sufficiently high quality that you cannot tell the difference without carefully observing the details. Here are some specific scenes in which you can fully enjoy shooting with an APS-C size camera.
Portraits, Snapshots
The telephoto effect of an APS-C size camera allows the photographer to capture a large central figure or subject. The narrow angle of view also makes it easier to take pictures that emphasize the subject by suppressing background information. For this reason, APS-C size cameras are useful in many situations for portrait and snapshot photography.
Try using an APS-C size camera when shooting in town or taking commemorative photos of family and friends.
Athletic events and sports
When photographing athletic events, it is necessary to take large pictures of children in the distance. This is where the APS-C size camera's ability to magnify the subject comes into play. Even from a distant spectator's seat, you will be able to take a powerful picture of a child that fills the entire angle of view.
The compact size of the APS-C size camera itself also has the advantage of reducing fatigue even after long hours of shooting. In other sports photography as well, the camera can capture the movements of the athletes in a large format, allowing you to take photos with a sense of realism.
Landscapes
Although an APS-C size camera produces less bokeh than a full-size camera, you can create works that take advantage of the ample bokeh by composing your shots in a creative way. Alternatively, if you take advantage of the small amount of bokeh, it is easy to focus on the entire landscape and take bright, beautiful pictures even with a relatively small f-number. Otherwise, the narrow angle of view is also suitable for capturing a particularly impressive part of the landscape.
Find a distinctive composition in a vast landscape and shoot it with an APS-C size camera.
Moon and starry sky
Although it is often thought that a full-size camera is essential for moon and starry sky photography because of the need for high-sensitivity photography in the dark, an APS-C size camera can also be used for high quality photography. On the other hand, it is possible to take advantage of the narrower angle of view to take pictures that emphasize the moon or constellations as subjects.
Find your own composition and take impressive photos. The principles of starry sky photography remain the same. Keep in mind key points such as adjusting exposure manually and using a tripod.
Birds
Birds are one of the scenes where an APS-C size camera is useful, as they require telephoto shooting. Bird photography generally requires an ultra-telephoto lens of approximately 300mm (35mm format equivalent) or more. For example, the TAMRON 150-500mm F5-6.7 (Model A057), when used with an APS-C size camera, provides a focal length equivalent to 225-750mm (35mm film equivalent). This will allow you to take pictures without being alarmed by wild birds.
Also, APS-C size cameras are more maneuverable than their full-size counterparts, allowing you to shoot quickly as the wild.
How to choose a lens for the APS-C size camera
After purchasing an APS-C size camera, it is important to select the appropriate lens. Here we will explain some important points on how to select a lens for the APS-C size.
Sensor size supported by the lens
There are two types of lenses for interchangeable-lens cameras: lenses for full-size cameras and lenses for APS-C size cameras.
Focal length and “35mm format conversion”
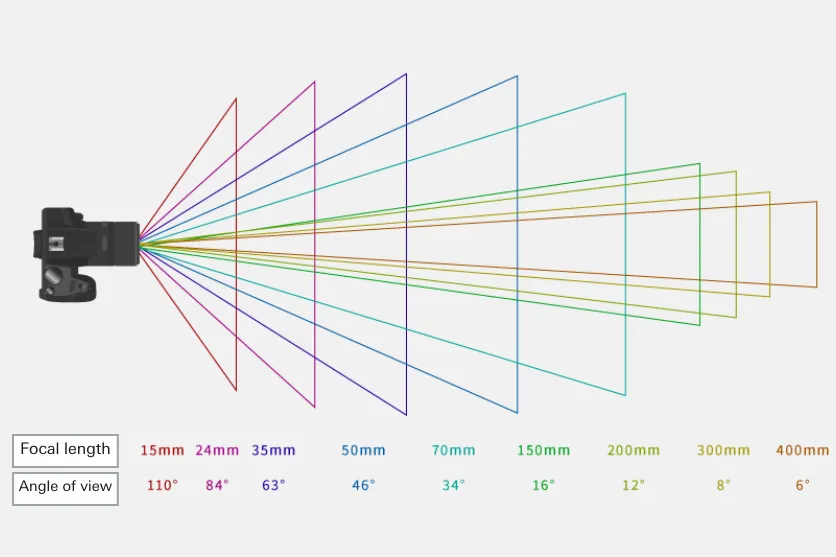
As mentioned above, lenses for APS-C size and lenses for full size have different angles of view even at the same focal length. Therefore, the angle of view is checked by converting the focal length of an APS-C size lens to that of a full-size lens (called “35mm format conversion”).
As a rough guide, the focal length of an APS-C size lens can be multiplied by approximately 1.5 to 1.6 times* to obtain a focal length equivalent to that of a full-size lens. The table below shows the typical relationship between the focal length of a lens for the APS-C size and its 35mm format equivalent focal length (figures in parentheses are 35mm format equivalent). Please use this as a reference when selecting a lens.
*35mm format equivalent magnification varies by camera manufacturer. The table below shows 1.55x as an example.
| Classification | Focal length of lenses for APS-C size |
|---|---|
| Wide Angle | 10mm (equivalent to 16mm) |
| 24mm (equivalent to 37mm) | |
| Standard | 35mm (equivalent to 54mm) |
| 50mm (equivalent to 78mm) | |
| Telephoto | 70mm (equivalent to 109mm) |
| 90mm (equivalent to 140mm) | |
| 150mm (equivalent to 233mm) | |
| Ultra-telephoto | 300mm (equivalent to 465mm) |
| 400mm (equivalent to 620mm) | |
| 600mm (equivalent to 930mm) |
The F-number (aperture value) is an indicator of the amount of light entering the camera's sensor through the lens, and the smaller the number, the brighter the aperture of the lens. The F-number at which the aperture is at its widest is called the maximum aperture F-number.
Therefore, the smaller the maximum aperture F-number, the easier the lens is to shoot in dark places and to take pictures with blurred backgrounds. This brightness is a big advantage when shooting in dark environments or when shooting fast-moving subjects.
The MOD represents the shortest distance at which the camera can focus on a subject. It is measured as the distance from the subject to the camera's sensor. If you get closer to the subject than the MOD, the camera will not be able to focus on the subject. A lens with a short MOD allows you to get very close to your subject and capture the details of flowers, insects, small objects, accessories, and other objects, making it possible to take impressive photographs. It is recommended that you choose a lens with a short MOD to broaden your range of expressions.
Zoom ratio
In a zoom lens, the ratio of the focal length at the telephoto end to the focal length at the wide-angle end is called the zoom ratio. For example, in the case of TAMRON 18-300mm F3.5-6.3 (Model B061), the zoom ratio is 300/18 = 16.6x. The larger the zoom ratio, the wider the angle of view a single lens can cover, making it useful in a variety of situations.
Therefore, if you are looking for a lens with high versatility, consider a lens with a large zoom ratio.
AF (Auto Focus)
AF (Auto Focus) performance is also an important factor when choosing a lens. Check to see if the lens can focus without stress and quickly follow a moving subject.
Especially when shooting sports, children, or animals, AF speed and accuracy are important because of the subject's active movement. If you will also be using the camera for video recording, it is also recommended that you check the AF's quietness.
VC (Vibration Compensation)
APS-C size cameras are often useful for telephoto shooting, but it is important to note that telephoto lenses are prone to camera shake. A lens equipped with an in-lens VC (Vibration Compensation) mechanism will effectively suppress the occurrence of camera shake. The VC mechanism is particularly effective when shooting outdoors or in situations where a tripod cannot be used.
Understand the characteristics of the APS-C size and choose the lens that best suits your needs
APS-C size cameras have features and advantages that differ from those of full-size cameras, such as being compact, easy to handle, and suitable for telephoto photography. Choose the best lens from among APS-C compatible lenses to enjoy photography with ease.

Lens Featured in this Impression
-

-
11-20mm F/2.8 Di III-A RXD b060(Model )
Product Page | 11-20mm F/2.8 Di III-A RXD (Model B060) is the world's first compact, lightweight F2.8 ultra wide-angle zoom lens for Sony E-mount APS-C mirrorless cameras. Can be a great choice for video shooting.
-

-
17-70mm F/2.8 Di III-A VC RXD b070(Model )
The 17-70mm F/2.8 Di III-A VC RXD (Model B070) is a large-aperture standard zoom lens for APS-C format mirrorless cameras. With a focal length range of 17mm to 70mm (a full-frame equivalent of 25.5-105mm) for daily use, this achieves a 4.1x zoom. The optical design ensures high resolution and high contrast not just in the center of the image but also in corners and at the edges. The quiet AF drive motor and the VC image stabilization mechanism facilitate hand-held shooting. In addition, by counteracting focus breathing, the 17-70mm F2.8 empowers users' expression of their creative intentions to the fullest degree. This highly practical lens allows you to easily enjoy the high image quality of a large F2.8 aperture for both still and video shooting.
-

-
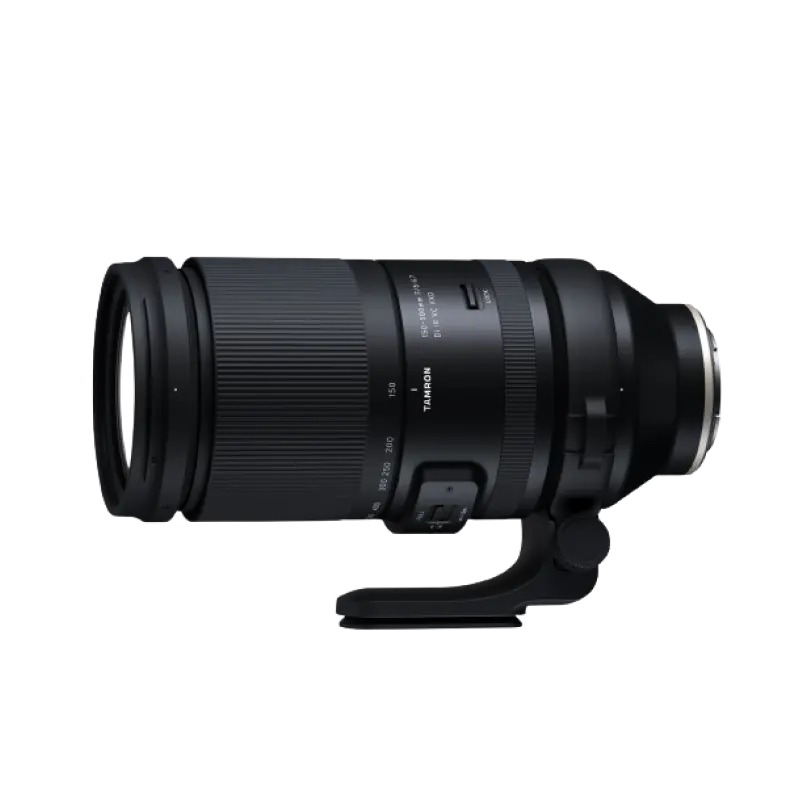
150-500mm F/5-6.7 Di III VC VXD X a057x(Model )
The 150-500mm F/5-6.7 Di III VC VXD (Model A057) is compact enough to be handheld while maintaining a focal length of 500mm on the telephoto end. It allows users to easily enjoy the world of the 500mm ultra-telephoto lens while maintaining its high image quality. The high-speed, high-precision AF with excellent tracking performance and the VC mechanism support handheld shooting in the ultra-telephoto range.
-

-
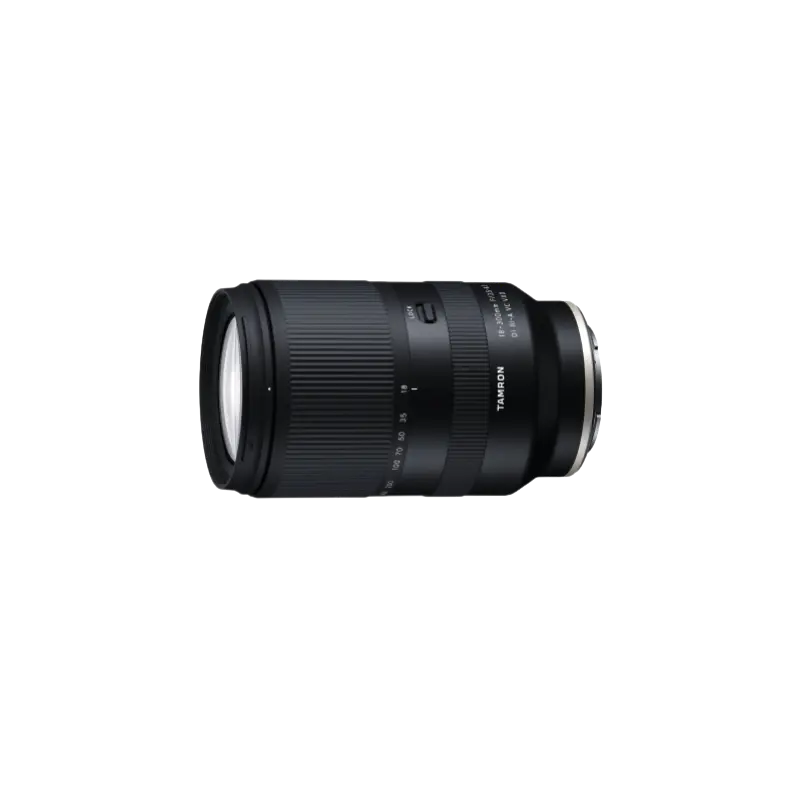
18-300mm F/3.5-6.3 Di III-A VC VXD b061(Model )
The 18-300mm F/3.5-6.3 Di III-A VC VXD (Model B061) achieves 16.6x zoom and is equipped with the VXD for a quiet and agile AF drive. The optical construction includes several special lens elements, specifically four LD (Low Dispersion) and three hybrid aspherical lens elements. These elements help to produce clear, sharp images from the center to the corners and deliver top-level image quality in its class. It is enabled close-up shooting and is equipped with the VC system. The 18-300mm F/3.5-6.3 makes photography more fun because you can use it in an unlimited number of situations. It’s so versatile, it will inspire you to push your creativity further and further.